Best Practices for Privacy-Compliant Apps and Websites in Canada

by BrainStream Chief User Experience Officer Yung-Wen Cheng
Developers creating apps and websites for Canadian users must align with the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA), Canada’s federal privacy law. Compliance begins with privacy by design—embedding data protection into the architecture of digital products from the outset. This includes collecting only necessary data, clearly communicating privacy policies, and obtaining meaningful user consent (Office of the Privacy Commissioner of Canada, 2023).
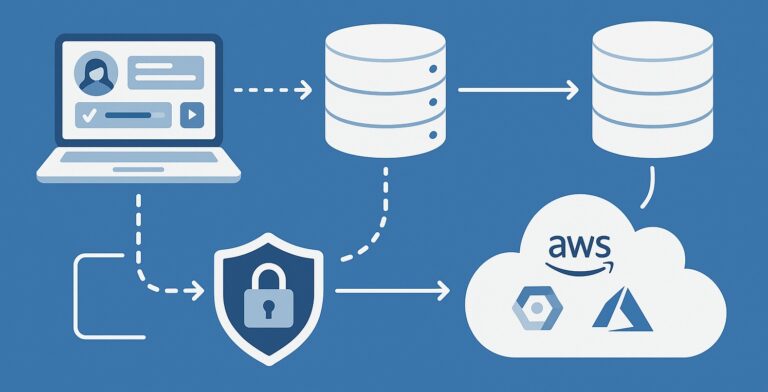
Use secure coding practices to prevent breaches, such as input validation, encryption, and secure session management. Encrypt data in transit and at rest using industry standards like TLS 1.2+ and AES-256. Conduct regular security audits and penetration tests to identify vulnerabilities early.
Developers must also enable users to access, update, or delete their personal information and ensure third-party services comply with Canadian privacy standards. When using analytics tools or cloud services, verify where data is stored and whether it crosses borders, which may trigger additional compliance obligations (Government of Canada, 2022).
Finally, stay updated. Privacy laws evolve, and provinces like Québec have introduced stricter frameworks (e.g., Law 25). Regular reviews and training help ensure ongoing compliance and build user trust.
References:
• Office of the Privacy Commissioner of Canada: https://www.priv.gc.ca
• Government of Canada, PIPEDA Guidelines: https://www.ic.gc.ca/eic/site/ecic-ceac.nsf/eng/h_00027.html